⚡ What Is a Phase Failure?
A phase failure (or phase loss) occurs when the voltage in one or more of the electrical phases drops to, or near, zero. In three-phase systems, this imbalance can cause equipment malfunction, reduced efficiency, or complete motor failure if not detected quickly.
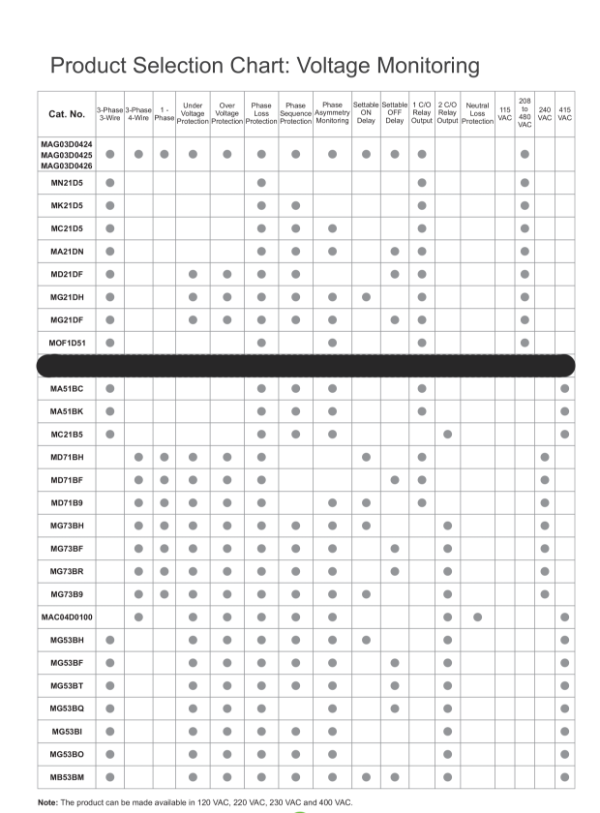
🔌 What Is a Phase Failure Relay?
A Phase Failure Relay is a protective monitoring device used to detect abnormalities in the electrical supply — typically across a three-phase network, though some can be used for single-phase systems. These relays monitor multiple fault conditions including:
- Complete Phase Loss
- Under Voltage
- Over Voltage
- Incorrect Phase Sequence
- Phase Asymmetry (imbalance)
- Neutral Loss
They are also known as Line Monitoring Relays, Supply Monitoring Relays, Phase Protection Relays, or 3-Phase Voltage Monitoring Relays. Most Phase Failure Relays operate on 3-phase supplies, with or without a neutral connection.
⚙️ How Do Phase Failure Relays Work?
Phase Failure Relays feature one or more relay outputs, typically configured in a fail-safe mode. When supply voltages remain within acceptable limits, the relay is energised, allowing normal circuit operation. If a fault occurs — such as phase loss, under or over-voltage — the relay de-energises, opening the circuit and protecting downstream machinery from damage.
🚨 Common Phase Failure Fault Conditions
Phase Loss
This occurs when one or more phases are missing. A motor may stall, fail to start, or continue running under high load imbalance, drawing up to 600% more current. This excessive current leads to overheating — according to Monzinger’s Rule, every 10% increase in operating temperature halves a motor’s lifespan. Heat is your enemy!
Under Voltage
When one or more phases drop below the preset limit, motors compensate by drawing more current. Continuous operation under undervoltage conditions causes insulation stress and premature wear.
Over Voltage
Excessive voltage in any phase accelerates insulation breakdown and may cause permanent motor damage.
Phase Sequence
Incorrect phase connection reverses motor rotation direction, which can damage pumps, conveyors, or mechanical couplings.
Phase Asymmetry
An uneven load distribution between phases exceeding 5% imbalance leads to overheating, vibration, and mechanical stress. Only relays with Phase Asymmetry Monitoring can detect this condition.
Neutral Loss
Neutral disconnection can result in downstream single-phase equipment being exposed to double voltage (up to 2× rated), damaging sensitive electronics.
🧠 How to Choose the Right Phase Failure Relay
- Identify your supply type:
A 3-wire relay measures phase-to-phase voltage (typically 400–415 V), while a 4-wire relay measures phase-to-neutral voltage (230–240 V).
- Decide on the number of outputs:
Single or double-pole changeover outputs are standard. For additional contacts, use auxiliary or slave relays.
- Define the monitoring functions required:
Phase loss is standard, but options like under/over-voltage and phase sequence vary by model.
Charter Controls offers over 30 different Phase Failure Relays ex-stock in the UK — all available for next-day delivery and backed by expert technical support. Custom options are also available upon request.
🔗 Related Blogs
Need help selecting the right Phase Failure Relay for your application? Contact our technical team or call us on 01424 850660 — we’re here to help.